The California Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) houses an Investigations Division that investigates suspicious acts in order to protect DMV programs and the interests of the Department and the public. The Division’s investigations primarily focus on cases of
The DMV Investigations Division has approximately 250 investigators assigned to various district and satellite office locations.
DMV investigators typically partner with
- other DMV field offices,
- local law enforcement, and
- other state agencies in the performance of their duties.
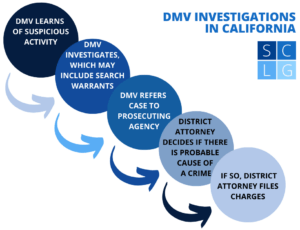
Although investigators have peace officer powers under California law, the DMV itself cannot prosecute suspects for a crime. California state prosecutors determine whether or not the state should file criminal charges against a suspect.
Depending on the facts of a case, a DMV investigation may result in:
- criminal or administrative actions against a suspect,
- the deterrence of criminal behavior,
- securing DMV documents and data, and
- the disruption of criminal schemes and operations.
Our California DMV hearing attorneys and criminal defense attorneys will highlight the following in this article:
- 1. What are DMV investigations?
- 2. What issues does the DMV investigate?
- 3. Can the DMV prosecute suspects for a crime?
- 4. What are the possible consequences of a DMV investigation?

The Investigation Division of the DMV Investigates cases of odometer tampering, as well as fraud and other cases.
1. What are DMV investigations?
According to the California DMV website, the Investigations Division protects the programs and interests of the DMV and public/consumer protection through:
- active fraud/counterfeit detection,
- investigation,
- audit, and
- enforcement services.1
DMV investigators perform a wide variety of duties. Some of these include:
- conducting surveillance and undercover operations,
- preparing and serving search and arrest warrants,
- participating in joint task force assignments with local, state, and federal law enforcement agencies, and
- computer forensics.2
The Investigation Division also provides training and education, at no cost, to:
- allied law enforcement and government agencies,
- civilian organizations,
- businesses,
- consumer outreach programs, and
- DMV employees and DMV office staff members.3
2. What issues does the DMV investigate?
The DMV Investigation Division focuses most of its office and field investigations on:
- altered and counterfeit documents (for example, a forged driver’s license or forged license plates),
- identity theft,
- odometer fraud,
- auto theft,
- counterfeit identification cards/id cards,
- vehicle registration fraud,
- financial crimes,
- misuse of person parking placards,
- consumer/employee fraud,
- fraud by vehicle-related businesses, and
- fraud within the automobile industry and by vehicle dealers.
As to the latter, one example of fraud by auto dealerships is the act of curbstoning.
“Curbstoning” is when vehicle dealers pose as private sellers to sell a car. The act allows unethical dealers and motor carriers to avoid having to comply with the regulations that apply to car dealers. To buyers, the act could result in the purchases of autos with bad vehicle titles.
3. Can the DMV prosecute suspects for a crime?
No. DMV investigators have peace officer powers under California law.4 For example, they can execute search warrants and arrest warrants.
But California state prosecutors determine whether the state should file criminal charges against a person suspected of a crime. In making this decision, a prosecutor has the responsibility of deciding whether the evidence in a case is sufficient enough to secure a conviction beyond a reasonable doubt.
4. What are the possible consequences of a DMV investigation?
DMV investigators usually commence an investigation once they receive a complaint form. Other times, the DMV will initiate investigation efforts.
Depending on the facts of the case, a DMV investigation may result in:
- no disciplinary or criminal actions,
- criminal or administrative actions against a suspect,
- the deterrence of criminal behavior (by either internal employees or members of the public),
- breaking up or preventing criminal schemes or operations,
- the protection of the integrity of the DMV’s documents and data, and
- the curbing of counterfeit mill operations and identity theft.5
Legal References:
- California DMV website, “Investigations Offices.”
- DMV Investigations Division presentation, “Overview of DMV Investigations” (2015).
- See same.
- See, for example, California Vehicle Code 1655 VC and California Penal Code 830.3c PC.
- See, for example, DMV Investigations Division presentation, “Overview of DMV Investigations” (2015).
